Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes: Overview
This topic consists of concepts such as Optical Isomers or Enantiomers and Optical Isomerism, Nicol Prism and Plane Polarised Light, Le Bel - Van't Hoff Rule, Racemic Mixture, etc.
Important Questions on Stereochemical Aspects of Nucleophilic Substitution Reactions of Haloalkanes and Haloarenes
The structures shown here are related as being
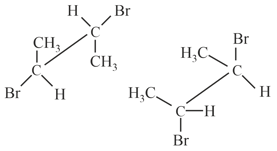
Which of the following structures represents a chiral compound?
What kind of reagent would be needed to resolve a racemic amine, such as 2-aminobutane?
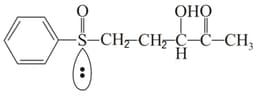
Number of chiral centers in the above molecule are:
A pure simple of -chlorobutane shows rotation of PPL by in standard conditions. When above samples is made impure by mixing its opposite form, so that the composition of the mixture become -form and -form, then what will be the observed rotation for the mixture.
If during a reaction, the product has the same general configuration of groups around the stereocentre as that of reactant. Such a reaction is said to proceed with:
Which of the following method is not used in the resolution of a racemic mixture?
Which of the following is taken as a reference to represent the relative configuration?
Which of the following compounds will give racemic mixture on nucleophilic substitution by ion? 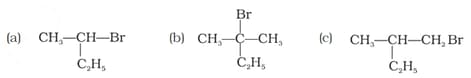
Racemic tartaric acid is optically inactive due to
Compound with molecular formula has chirality but on hydrogenation compound is converted into compound in which chirality disappear compound is:
How many chiral carbon atoms are present in 2, 3, 4- trichloropentane?
A solution of (−)−1-chloro-1-phenylethane in toluene racemises slowly in the presence of small amount of , due to the formation of
Which of the following molecules is achiral?
How many optically active isomers are possible for ?
The optically inactive compound is
The number of asymmetric carbon atoms in glucose are
Among the following serine is :-

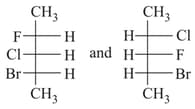 both are :-
both are :-